- Blog
- biodiversity
- What is...
What is biodiversity and why is it important?
Sep 24, 2021 | written by: Lara Zambonelli
The term biodiversity refers to all species of plants and animals on the planet, their genetic differences, and the ecosystems they form. In this article, we look at why people have started talking about biodiversity instead of nature, where in the world this richness is concentrated, and how we can preserve it.
What does biodiversity mean?
The term biodiversity, as an abbreviation of biological diversity, was coined in 1988 by the American entomologist Edward O. Wilson, who gave it the following definition:
“Biodiversity is the totality of all inherited variation in the life forms of Earth, of which we are one species [1].”
E.O. Wilson
Biodiversity has three levels:
- genetic diversity;
- species diversity;
- ecosystem diversity.
Why is biodiversity important?
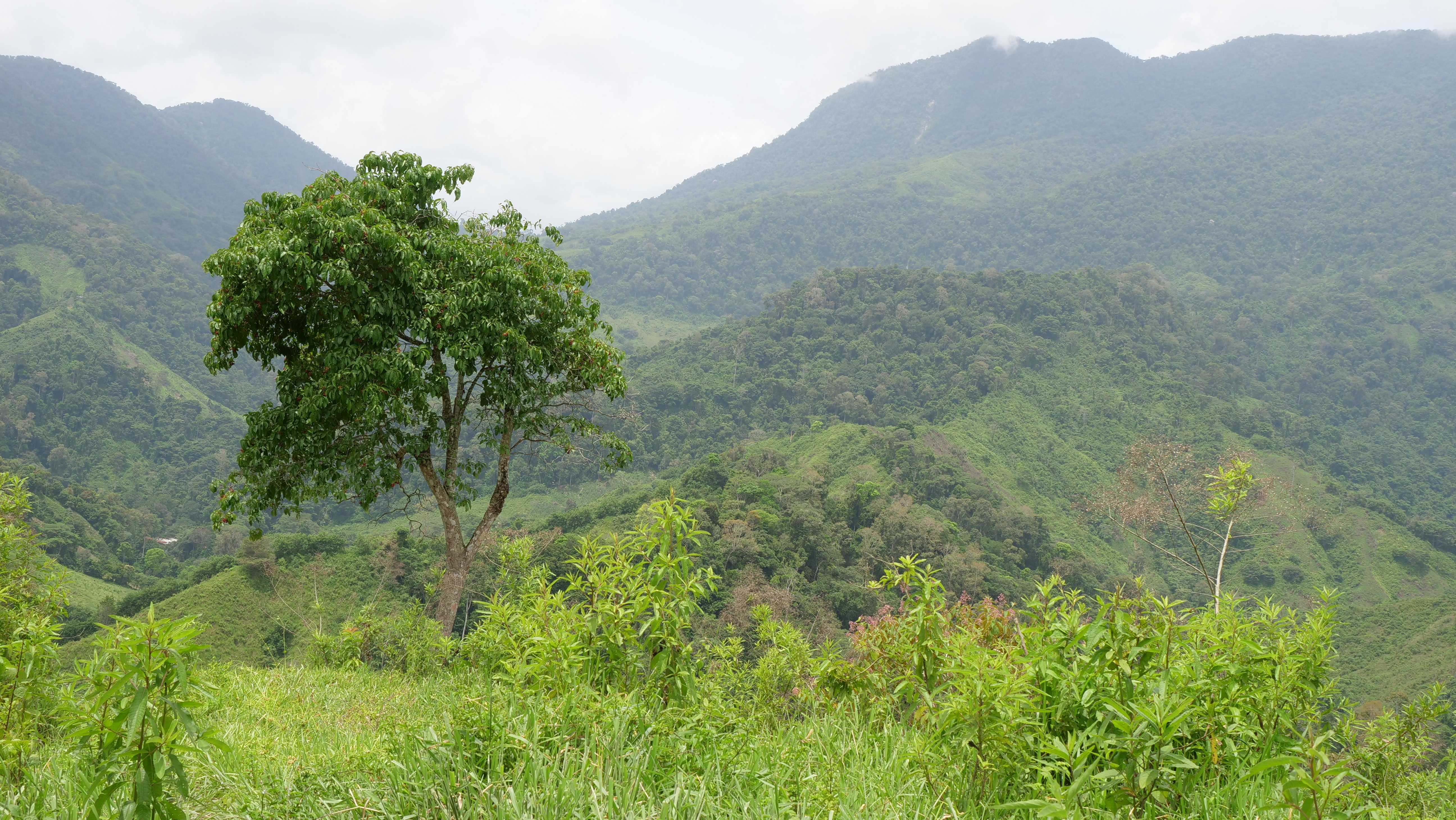

(A shot from one of the Treedom project areas in Colombia)
Today there are 1.74 million species of animals, plants, fungi and microorganisms on Earth, not counting all those that have not yet been discovered.
In addition to the intrinsic value of this incredible richness, biodiversity is also extremely important from a pragmatic perspective.
At least 40% of the world's economy is derived from biological resources (raw materials, energy resources, crops, animals, etc.). Moreover, with greater biodiversity comes an increased possibility of new medical discoveries, new economic developments and new ways of responding to climate change.
What are megadiverse countries?
Biodiversity is not evenly distributed on Earth: it increases as you move from the poles towards the equator. According to Conservation International, an environmental NGO, 70% of the world’s flora and fauna is found in just 17 countries. Many of these countries are also home to a large number of endemic species, i.e. species which only live in that specific place.
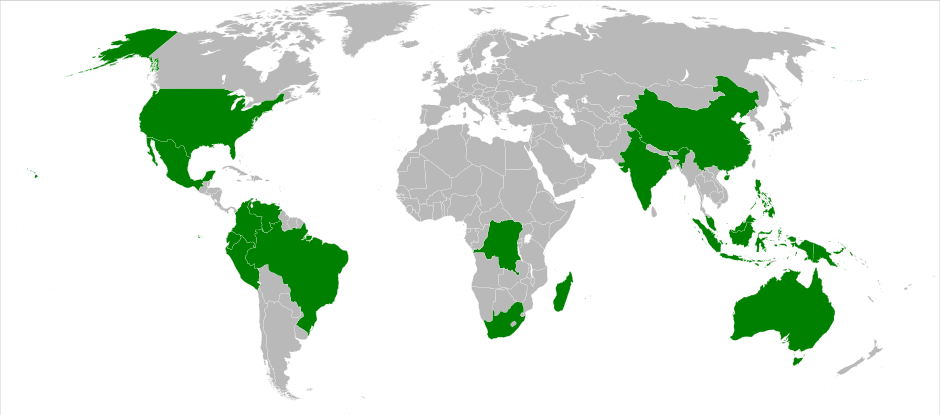
These 17 countries are referred to as megadiverse, and they are:
- Australia
- Brazil
- China
- Colombia
- Ecuador
- Philippines
- India
- Indonesia
- Madagascar
- Malaysia
- Mexico
- Papua New Guinea
- Peru
- DR Congo
- United States
- South Africa
- Venezuela
How is biodiversity protected?
There are countless public and private initiatives, NGOs and international organisations whose aim is to protect biodiversity.
As early as 1964, for example, the Red List of Threatened Species [3] was established. This tool is used by governments to track progress with regard to biodiversity.
Today, however, it is clear that the best way to preserve biodiversity is to save ecosystems rather than individual species. To do this, we need to reconcile the well-being of ecosystems with the demands of human life.
Why are trees good for biodiversity?
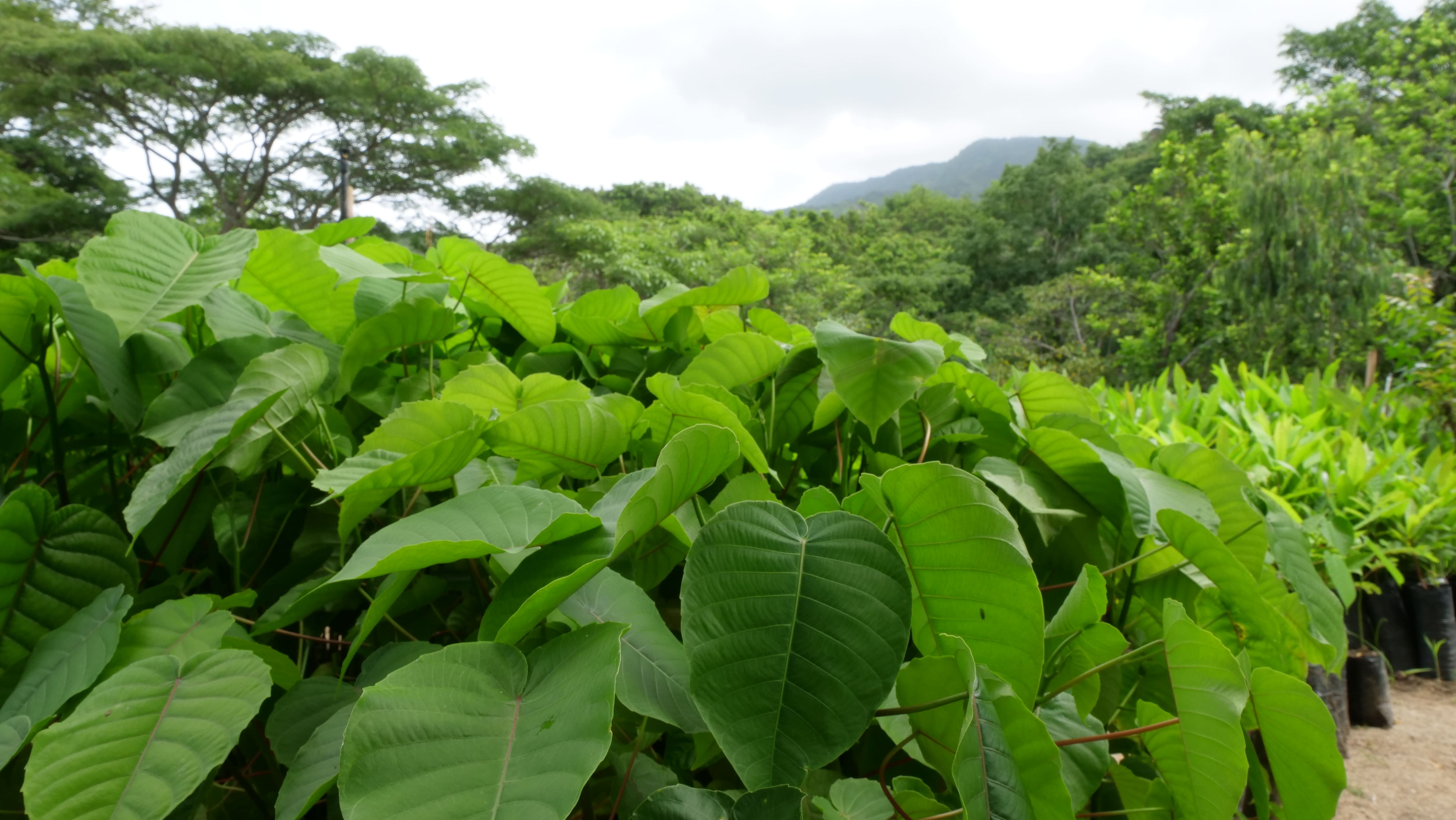

(One of Treedom’s nurseries in Latin America, where trees are grown before being planted)
If they’re planted in the right way, trees can be powerful allies of biodiversity.
Treedom plants trees in agroforestry systems, integrating them with existing annual crops (such as maize, beans, wheat, etc.). This is an ancient method that mimics what occurs spontaneously in nature, with surprising results:
- the positive synergy created between trees and crops promotes the productivity of land, benefitting local communities;
- at the same time, the trees provide shelter and food for insects and animals.
Talking about “biodiversity” rather than “nature” serves a specific purpose: to remind us that the human species is only one of Earth's many species, and as such it is interconnected and interdependent [4] with the others.
To help preserve this richness, you can plant a tree with us.

